
Modern Aerospace Coating Removal: Protecting People and the Environment

Modern Industrial Coating Removal:
Protecting People and the Environment
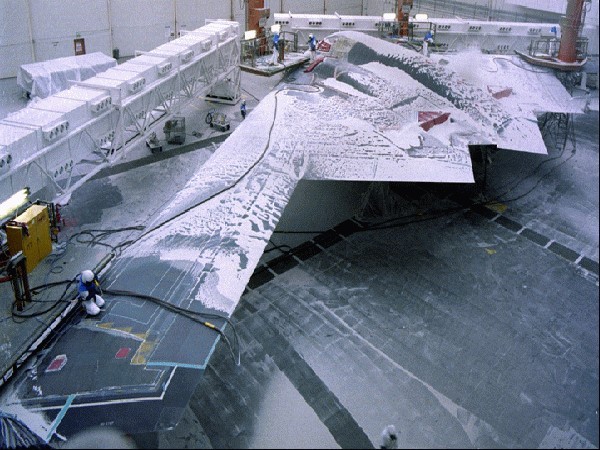
In the past, industrial brands had limited choices when it came to the products used for their industrial applications. Hazardous working conditions, dangerous chemicals, toxic waste, and environmentally-destructive processes were unfortunate occupational realities. For aerospace and automotive brands, removing paint coatings from metals and sensitive composites once required the use of toxic chemicals or hazardous manual sanding. Cleaning and deflashing parts required the handling and disposal of hazardous chemicals. These applications put both workers and valuable materials at risk.
Today, with advances in technology and a global focus on preserving our planet, companies are no longer forced to utilize these destructive and dangerous processes of the past.
Since 1901, Midvale Industries has been a pioneer for protecting both people and the environment, by leading the creation and evolution of processes to remove coatings, clean parts and increase efficiency in a safe and cost-effective way.
Multiple bio-based, renewable blasting mediums, developed by Midvale Industries and ADM, allow aerospace and automotive brands to quickly remove layers of coatings from sensitive materials or metals, in a safe and environmentally-friendly way. These abrasives, initially developed for military use, are as soft as a human fingernail, are corn starch based, and are a 100% renewable resource.
When utilized as part of an engineered blasting process, this process:
- Is 8-10 times faster than sanding
- Preserves component integrity and protects from material fatigue (common with traditional blasting)
- Eliminates dangerous toxic chemical exposure
- Eliminates the need for harmful hand-sanding and potential for HAVS (Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome)
- Decreases long-term production costs
Even in 1996, before green approaches became a major trend, Midvale was featured as a green solution for removing coatings from the B-2 Bomber, a unique military aircraft made almost entirely of sensitive carbon-graphite composite material.

Clients from coast-to-coast, including the US Navy and the US Coast Guard, utilize Midvale’s environmentally-friendly processes for coating removal, composite tool cleaning or metal bond deflashing projects of all sizes.



Midvale’s engineers are trained in developing custom, holistic finishing processes and serving as a strategic partner to our clients. In building and refining industrial processes, we search for bottlenecks, possible waste, and potential safety issues, and provide regular inspection reports on equipment and consumables. We offer training and troubleshooting for clients, working to build and streamline processes in the most efficient, cost-effective and safe way.



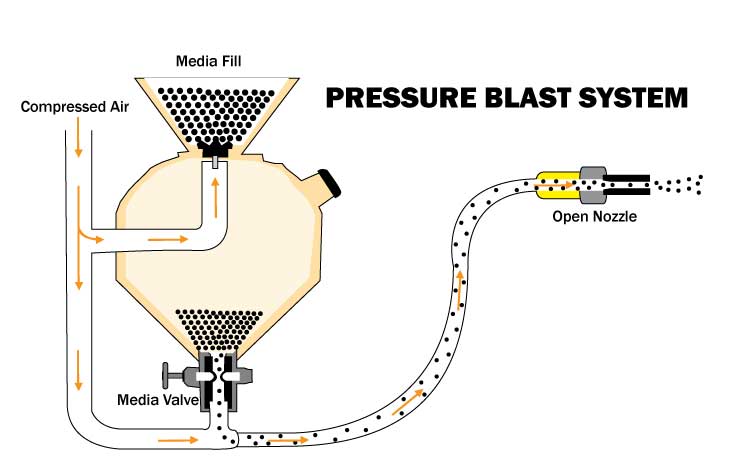
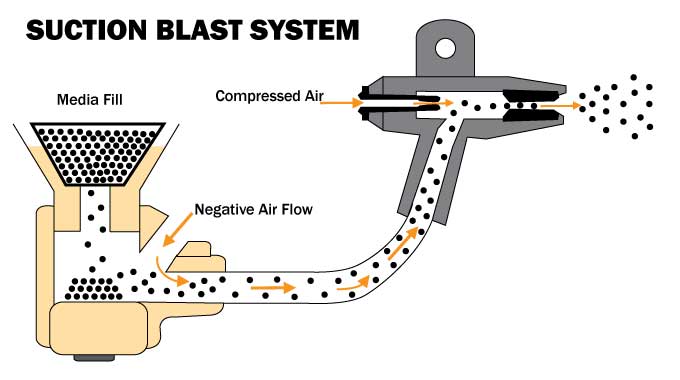












Recent Comments